Table of contents of the article
ToggleLemon scab is a fungal disease that leads to the appearance of ulcers and deformities on the surface of fruits. This article from the “WORLD OF PLANTS” website provides an explanation of the causes of the disease and effective methods of prevention and treatment.
Definition of anthraclose disease in lemon
- Name of the disease: Try lemon
- The scientific name: fawcetti
- Type of disease: Bacterial pathogen
- Disease family: Sphaceloma fawcettii
Lemon scab is a serious fungal disease that affects all varieties of lemon, and also affects all parts of the lemon tree.
Symptoms of anthraclosis in lemon
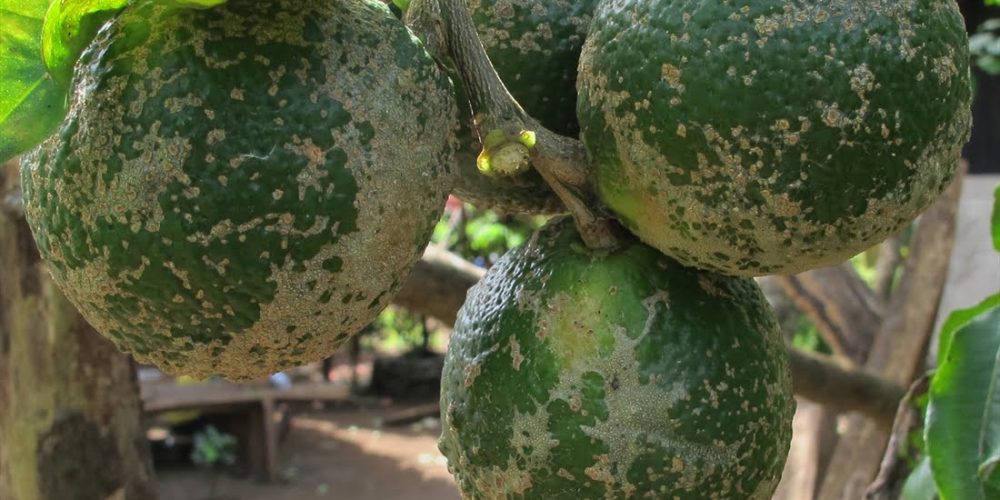
Light brown wart-like blisters or crusts form on the leaves, stems, and fruits. The scales are gray or pink at first and become darker as the infestation ages. Old lesions of the crust become rough to the touch and become cracked and fissured, while the leaves become stunted, wrinkled, and have irregular torn edges.

Life cycle of anthraclosis in lemon
Mushroom spores are produced in peels and then spread through wind and rain spray. Insects may also help spread it over long distances. The spores need 4 hours to germinate, after which they can become susceptible to infection. Leaves, stems, and fruits are infected when they are young, but they become resistant to infection when they are Full size.
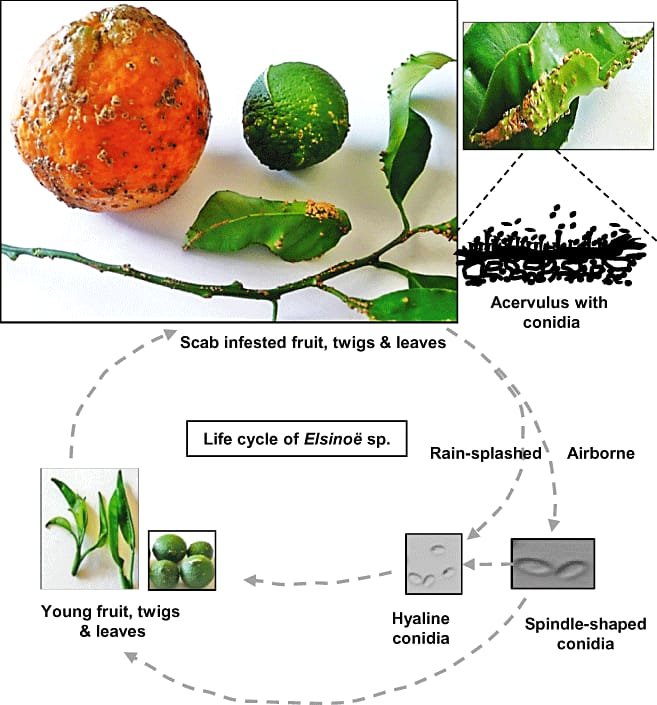
Causes of Anthracnose in lemon
Leaf moisture is the most important factor in determining infection. When conditions are appropriate, lemon leaves are susceptible to infection when the flow of new growth is less by 25%, and immature lemon fruits are more susceptible to infection than ripe ones.
Suitable conditions for the disease anthraclose in lemon
- Wet conditions favor the development of the disease.
- Most germs come from infected young lemon fruits.
- Temperature does not appear to have a significant effect on disease.
Losses due to disease
The fungus causes deformation of the leaves and causes an unattractive infection on lemon fruits. The infection reduces the market value of the fruits but is unlikely to affect the quality of production. The infection on seedlings in the nursery is more serious as it makes it difficult to graft, such as the rough lemon and lemon rangpur. , and the trifoliate poncerus.
Control of anthraclosis in lemon
- Fungicides can be used to control fungi. They should be applied to plants in nurseries at the beginning of leaf growth to prevent infection, but it is important that the instructions for use are followed carefully to avoid harming the plants or the environment.
- Copper (copper oxide) or chlorothalonil are suitable options.
- Treating mature lemon trees is not recommended, as they produce multiple crops such treatments are unlikely to be economical.
Preventive measures for Anthracnose in lemon
Prevention is the best way to control lemon scab. This can be achieved by selecting resistant varieties and applying good agricultural practices, establishing nurseries to produce seedlings and cuttings away from commercial farms where the disease may be present, and pruning trees regularly to remove sources of spores and improve air movement.
In conclusion, we would like to note that we, at the world of plants website, offer you all the necessary services in the world of plants, we provide all farmers and those interested in plants with three main services::-
- Artificial intelligence consulting service to help you identify diseases that affect plants and how to deal with them.
- Blog about plants, plant diseases and care of various crops ... You are currently browsing one of her articles right now.
- An application that provides agricultural consultations to clients, as well as a service for imaging diseases and knowing their treatment for free – Click to download the Android version from Google Play Store، Click to download the IOS version from the Apple App Store.
References:
Lemon growing manual – NSW Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development
Elsinoë fawcettii (citrus scab) – cabidigitallibrary




