Table of contents of the article
ToggleCitrus canker is a bacterial disease that affects citrus trees, causing cankers to appear on the fruits and leaves, reducing their quality and productivity. In this article on your website, WORLD OF PLANTS, we will discuss the causes and symptoms of this disease and how to prevent it to protect your crop.
Symptoms of citrus ulcer
English name: Canker Citrus
Scientific name: Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri
Type of disease: a bacterial disease
Platoon: Xanthomonadaceae
Citrus canker is a highly contagious disease that affects all cultivated citrus varieties, including lemons. The main symptom is the formation of swollen lesions, brown or light brown, on leaves, stems and fruits. These lesions can be circular or irregular in shape and surrounded by a yellow halo. As the disease progresses, the lesions may become crusty or leathery, and the central area can fall off, giving the lesions a volcanic appearance. Severe infestations can result in defoliation, death of terminal shoots, and premature drop of fruit.
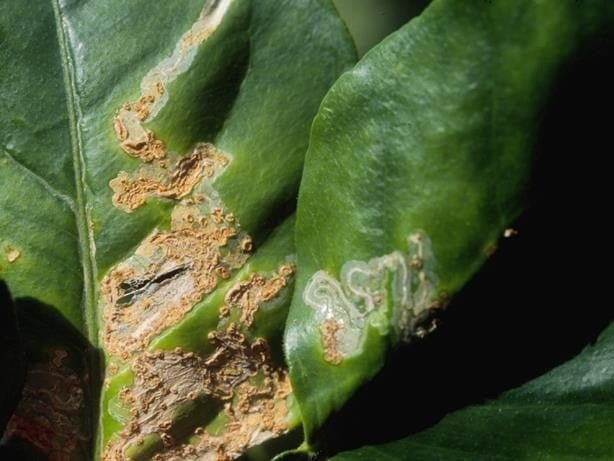
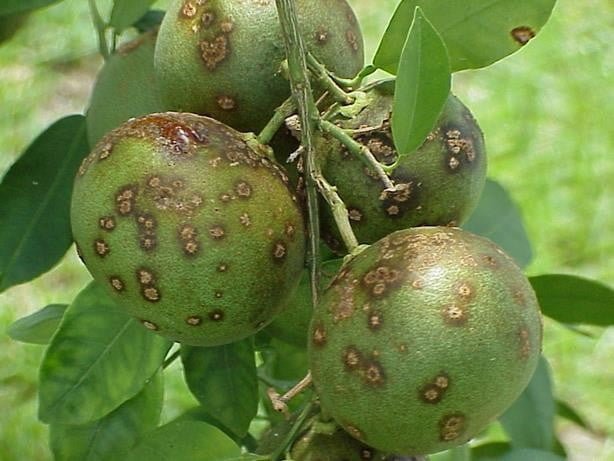
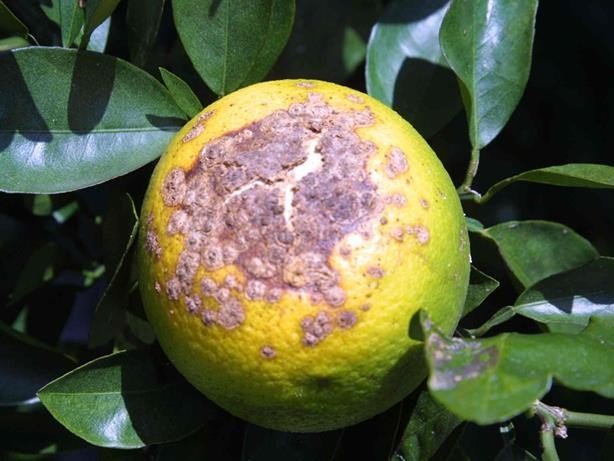
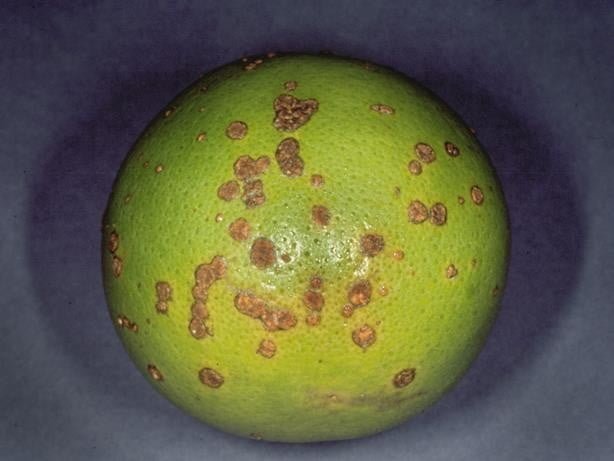

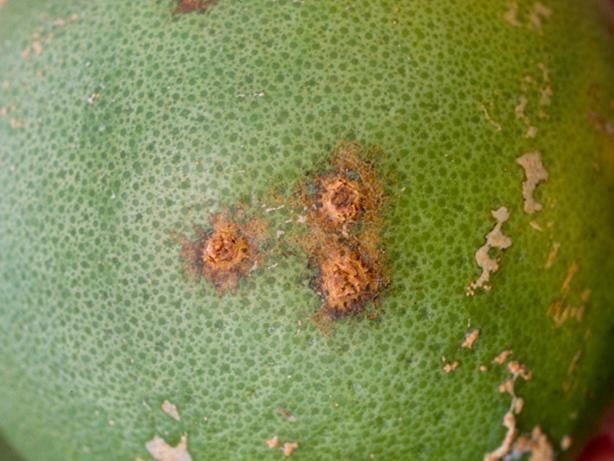


Causes of citrus ulceration
Citrus canker is caused by the bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri. The bacteria can survive in infected plant material such as leaves, branches and fruits, as well as contaminated soil and various surfaces, including tools and equipment used in citrus orchards.
Conditions conducive to the spread of citrus canker disease
Citrus canker is spread primarily by wind-driven rain, which can spread bacteria cells over great distances. The disease can also be transmitted through infected plant material or contaminated tools and equipment, in addition to human activity in citrus orchards. Warm, humid conditions and periods of heavy rainfall or sprinkler irrigation favor the spread and development of the disease. Young, tender plant tissues are more susceptible to injury than mature, hardened tissues.
Citrus canker disease cycle
The citrus canker disease cycle begins with the introduction of pathogenic bacteria into citrus orchards, where bacteria can enter the plant through natural openings such as stomata or wounds caused by wind, cold, or mechanical damage. Once they enter the plant, the bacteria multiply and cause lesions to form on the leaves, branches and fruits. During periods of wet weather, bacteria swarm from pests and can be spread by wind, rain or splashing water to other parts of the plant or to nearby trees. Bacteria can also survive in plant debris, soil, or on contaminated surfaces, posing potential sources of infection for future agricultural seasons.
Citrus canker losses
Citrus canker can cause significant economic losses in the production of lemons and other citrus fruits. The disease can reduce fruit yield and quality, as well as weaken trees, making them more susceptible to disease and other environmental stresses. In severe cases, the disease can result in complete crop loss for the season.
Strategies to combat citrus canker
Citrus canker control strategies include strict quarantine measures, removal and destruction of infected plant material, and use of disease-free seedlings. Copper-based bactericides can be applied to protect healthy trees, but their effectiveness is limited once the disease becomes established. Agronomic practices such as proper pruning and orchard cleanliness can help limit the spread of the disease.
In conclusion, we would like to note that we, at the world of plants website, offer you all the necessary services in the world of plants, we provide all farmers and those interested in plants with three main services::-
- Artificial intelligence consulting service to help you identify diseases that affect plants and how to deal with them.
- Blog about plants, plant diseases and care of various crops ... You are currently browsing one of her articles right now.
- An application that provides agricultural consultations to clients, as well as a service for imaging diseases and knowing their treatment for free – Click to download the Android version from Google Play Store، Click to download the IOS version from the Apple App Store.




