Table of contents of the article
ToggleSesame leafworm is considered one of the insect pests that threaten sesame cultivation. In this article on your website, World of Plants, we learn about its life cycle and ways to combat it.
Symptoms of sesame leafworm
- Scientific name : Acherontia atropos
- Type of disease: Insect
- the family : Lepidoptera
- It attacks all parts of the plant (except the roots), including the leaves and stems, as well as the flowers and fruits.
- The infection is characterized by the entanglement of the upper leaves of plants with each other with fine threads that spin them and transform them into the pupal stage.
- This insect causes the fall of many flowers and young pods and the drying of the terminal leaves

Description of sesame leafworm
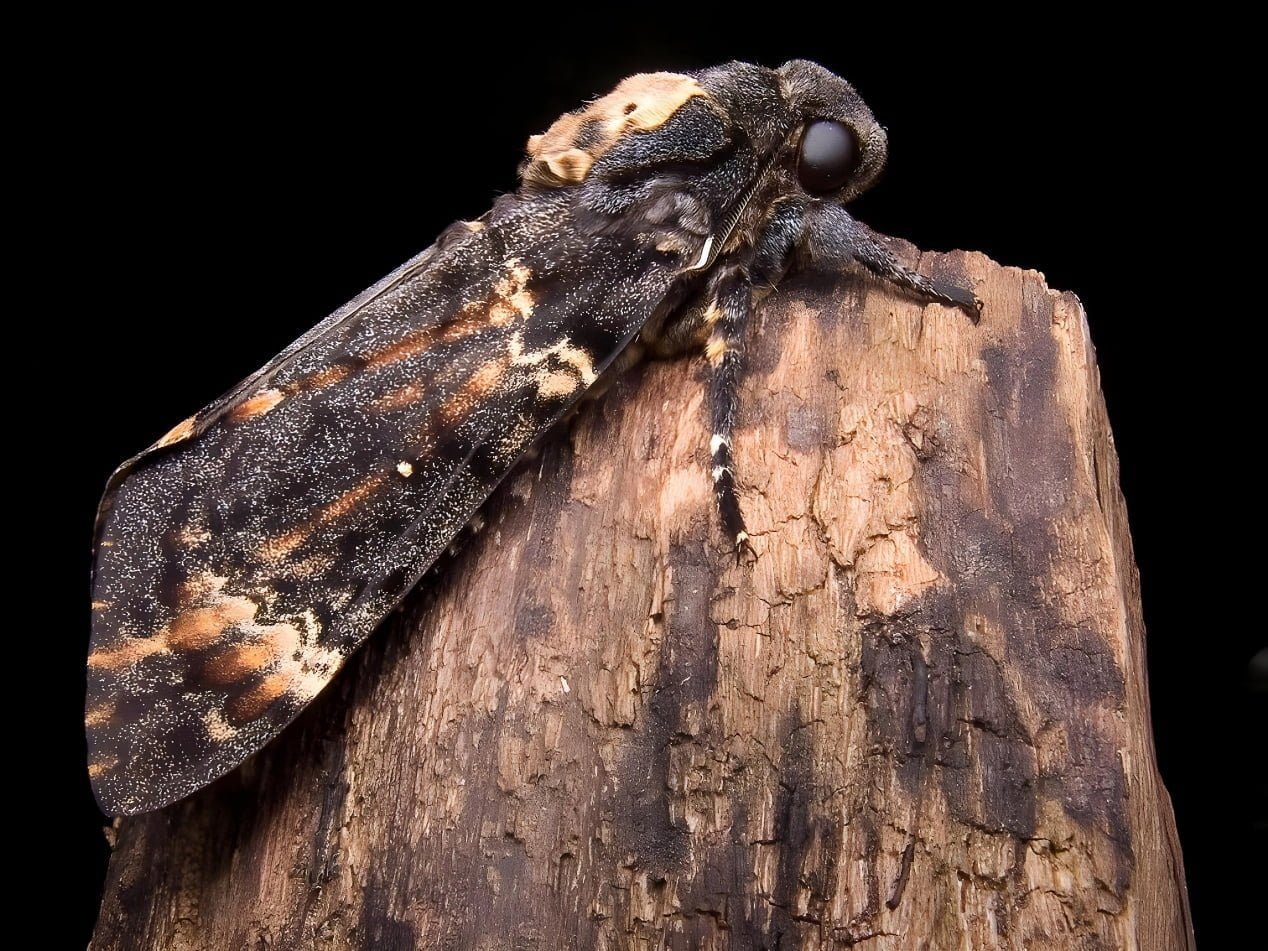
- The adult insect is about 5-6 cm long, and the distance between the tips of the wings is about 11-12 cm. The front wings are brown, crossed by white transverse lines. The hind wings are yellow, surrounded on the outside by two black lines. The chest has a yellow shape resembling a skull.
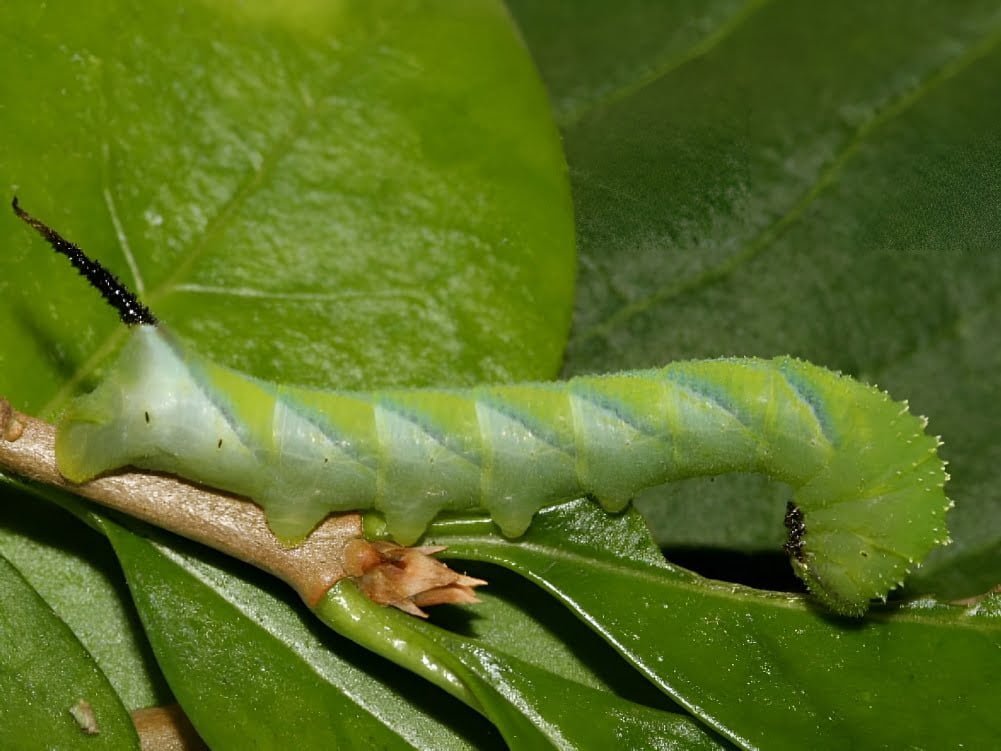
- The larva: It is 10-15 cm long when fully developed and is light green in colour. Its body has a wide, sky-blue stripe on its dorsal side. On both sides there is a black stripe alternating with a yellow one. At the end of the abdomen, there is a dorsal horn with granular nipples.
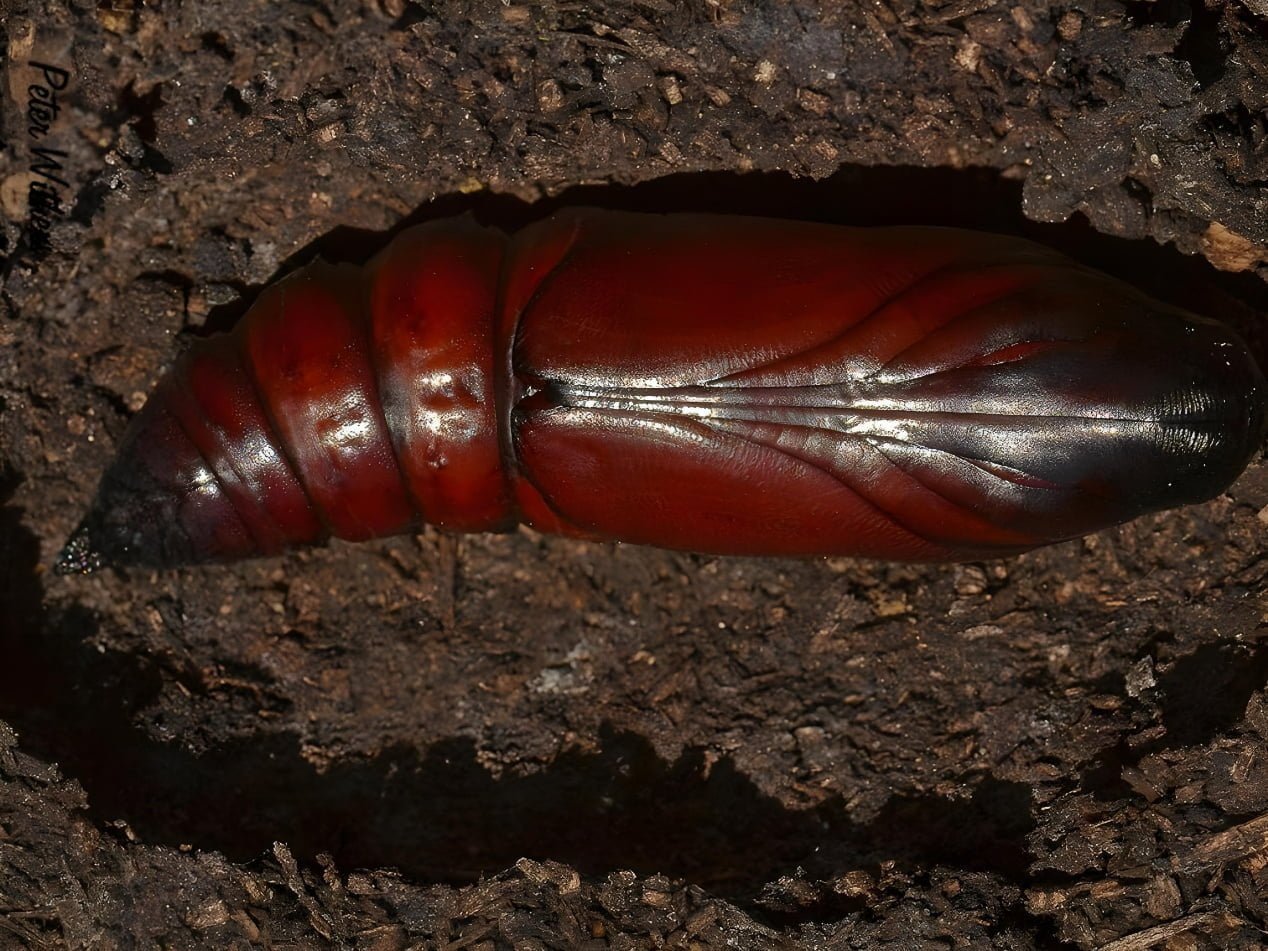
- The pupa: It is located inside a clay cell inside the soil at a depth of 2 cm. It is brownish-red in color, and its length is about 6 cm.



Causes of sesame leafworm
- The presence of infected fields.
- Moderate heat, this butterfly is active in February-September
- The presence of harmful weeds and not removing them.
- Rainfall (more dangerous in rainy seasons).
- The presence of dried or diseased buds.
- Irrigation is not regulated.
- Lack of interest in agricultural operations such as cultivation, hoeing and fertilization.
Suitable conditions for the spread of sesame leafworm
- The presence of insect hosts next to the infected pepper field, such as potatoes, sesame, legumes, and nightshades, and the insect was recorded on some ornamental plants and some herbs.
- The presence of a beehive and a water source.
Sesame leafworm development cycle
- The insect spends the winter hibernation period in the pupal stage in the soil at a depth of 10-20 cm. The insect resumes its activity in the spring, and this happens at the end of March and the beginning of April. The butterflies feed on the nectar of the flowers and then mate.
- The fertilized females behave as solitary egg-layers, and the females lay eggs on the leaves. The average number of eggs laid by one female is about 200 eggs.
- The duration of fetal development is 7-14 days.
- The larvae have 5 ages, and the duration of larval development is about 20 days on average.
- Fully-developed larvae embed in the soil at a depth of 10 cm, and the pupa remains dormant until the spring of next year. The insect has one generation per year.
Losses of sesame leafworm spread
The larvae feed voraciously on the leaves and eat the entire leaf except the main veins, and may strip the plant of its leaves.
Control strategy against sesame leafworm
Preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of the disease
- Deep plowing of the soil in winter to eliminate the overwintering phase.
- Removing weeds and plant residues from the field
- Good fertilization of trees
- Irrigation regulation.
- Periodically monitor the field and ensure that there are no pests.
- Place plant traps as protection, such as sunflowers
Chemical and organic control recommendations against sesame leafworm
- Organic control
- Pick up the larvae by hand early in the morning
- Spiders and predatory birds, which are classified as lethal agents for the fourth and fifth larval stages of this pest.
- Chemical control:
- The insect is attacked by many insect parasites, including the larval parasite Compsilura Lydella stabulanusconsinnata from the order Diptera, Tachinidae family.
- Spraying plants when the beginning of infection appears with organic pesticides that have an infectious and contact effect.
In conclusion, we would like to note that we, at the world of plants website, offer you all the necessary services in the world of plants, we provide all farmers and those interested in plants with three main services::-
- Artificial intelligence consulting service to help you identify diseases that affect plants and how to deal with them.
- Blog about plants, plant diseases and care of various crops ... You are currently browsing one of her articles right now.
- An application that provides agricultural consultations to clients, as well as a service for imaging diseases and knowing their treatment for free – Click to download the Android version from Google Play Store، Click to download the IOS version from the Apple App Store.
References
- Ahirwar, R. M., Gupta, M. P., & Banerjee, S. (2008). Evaluation of natural products and endosulfan against incidence of Antigastra catalaunalis (Dup.) in sesame. Annals of Plant Protection Sciences, 16(1), 25-28.
- Jakhmola, S. S. (1983). Natural enemies of til leafroller and capsuleborer, Antigastra catalaunalis (Dup.). Bulletin of Entomology, 24(2), 147-148.
- Gupta, M. P., Rai, H. S., & Chaurasia, S. K. (2002). Incidence and avoidable loss due to leaf roller/capsule borer, Antigastra catalaunalis Dup. in sesame. Annals of Plant Protection Sciences, 10(2), 202-206.
- Yalawar, R., Acharya, V. S., & Hiremath, R. (2020). Bio efficacy of different insecticides against leaf webber and capsule borer, Antigastra catalaunalis (Dup.) on sesame. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 9(5), 90-93.
- Evaluation of natural products and endosulfan against incidence of Antigastra catalaunalis – indianjournals
- Natural enemies of til leafroller – cabidigitallibrary
- Incidence and Avoidable Loss due to Leaf Roller/Capsule Borer, Antigastra catalaunalis Dup. in Sesame – indianjournals
- Bio efficacy of different insecticides against leaf webber and capsule borer, Antigastra catalaunalis – phytojournal




