We provide you with everything necessary
In the world of plants
Accurate and effective consultations
Discover artificial intelligence and agriculture with the world of plants. We harness artificial intelligence in early detection of agricultural pests and provide consultations by agricultural specialists. You can now improve the care of your plants with confidence and sustainability. Discover the joy of gardening with the help of plant identification technology.
We provide you with everything necessary
In the world of plants
Accurate and effective consultations
Discover artificial intelligence and agriculture with the world of plants. We harness artificial intelligence in early detection of agricultural pests and provide consultations by agricultural specialists. You can now improve the care of your plants with confidence and sustainability. Discover the joy of gardening with the help of plant identification technology.

Product classifications

Fertilizers and fertilisers
Fertilizer is a substance added to the soil to help plants grow. Farmers use several types of fertilizers to produce abundant crops.

Home health
The most important types Insects And pests household Which we must eliminate when we discover its presence In our homes Are: cockroaches; bugs; ants; Albaras (distribution); Bed bug (mites).

Herbicides and weed killers
The best weed killers in recent years in the world are highly effective in combating all types of annual, perennial, delicate and broad-leaved weeds.
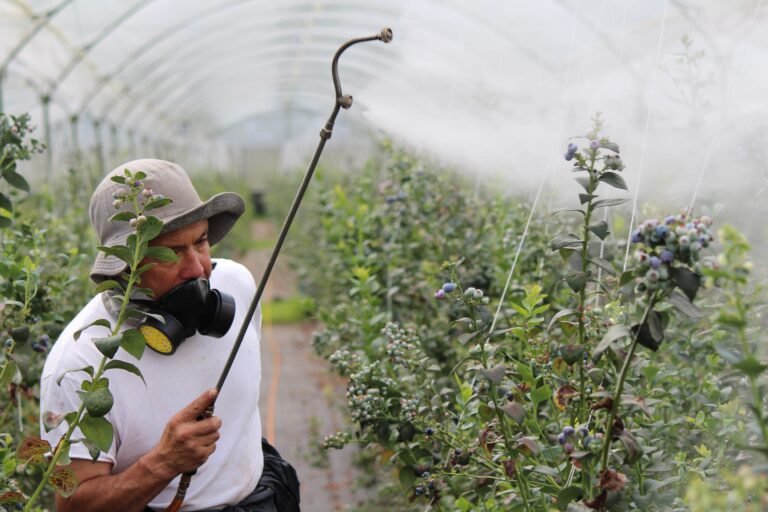

Pesticide
Most insecticides will be used to control insects or cutworms, as well as sucking and boring insects.

Fungicides and blights
The fungicide has a dual preventive and curative effect. It is quickly absorbed by the leaves or roots. It is used to combat downy mildew, root rot, wilt, blight, and canker.
Our products
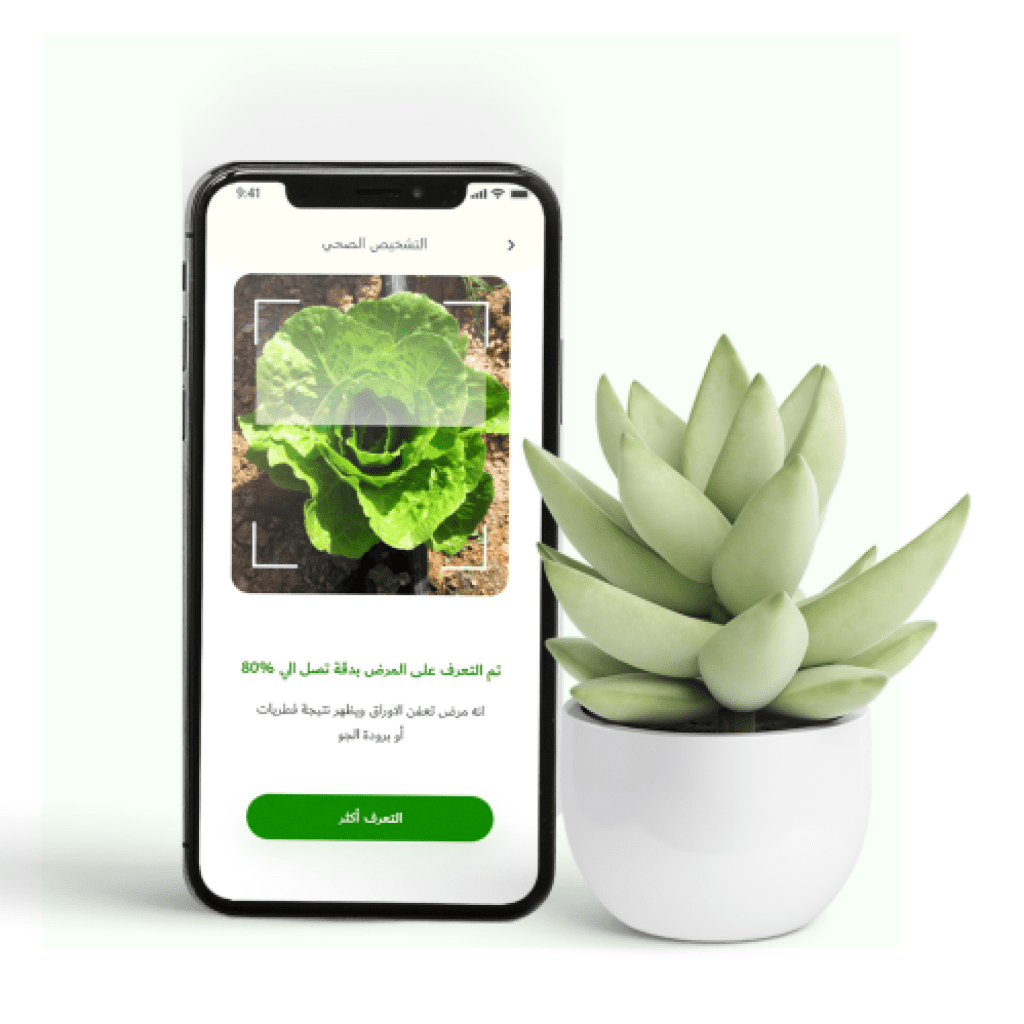
An application that identifies plant diseases and diagnoses plant problems
The Plant World app covers nearly 30 major crops and detects over 100 plant diseases.
Free-to-use plant care app identifies plant diseases and saves time
Treat your crops and enjoy higher yields with the Plant World app! Discover with us artificial intelligence and agriculture
The Botanist app turns your Android phone into a mobile crop doctor with which you can accurately detect pests and diseases in crops within seconds. The Botanist application is an integrated solution for crop production and management.
Download the app now to get the most out of it
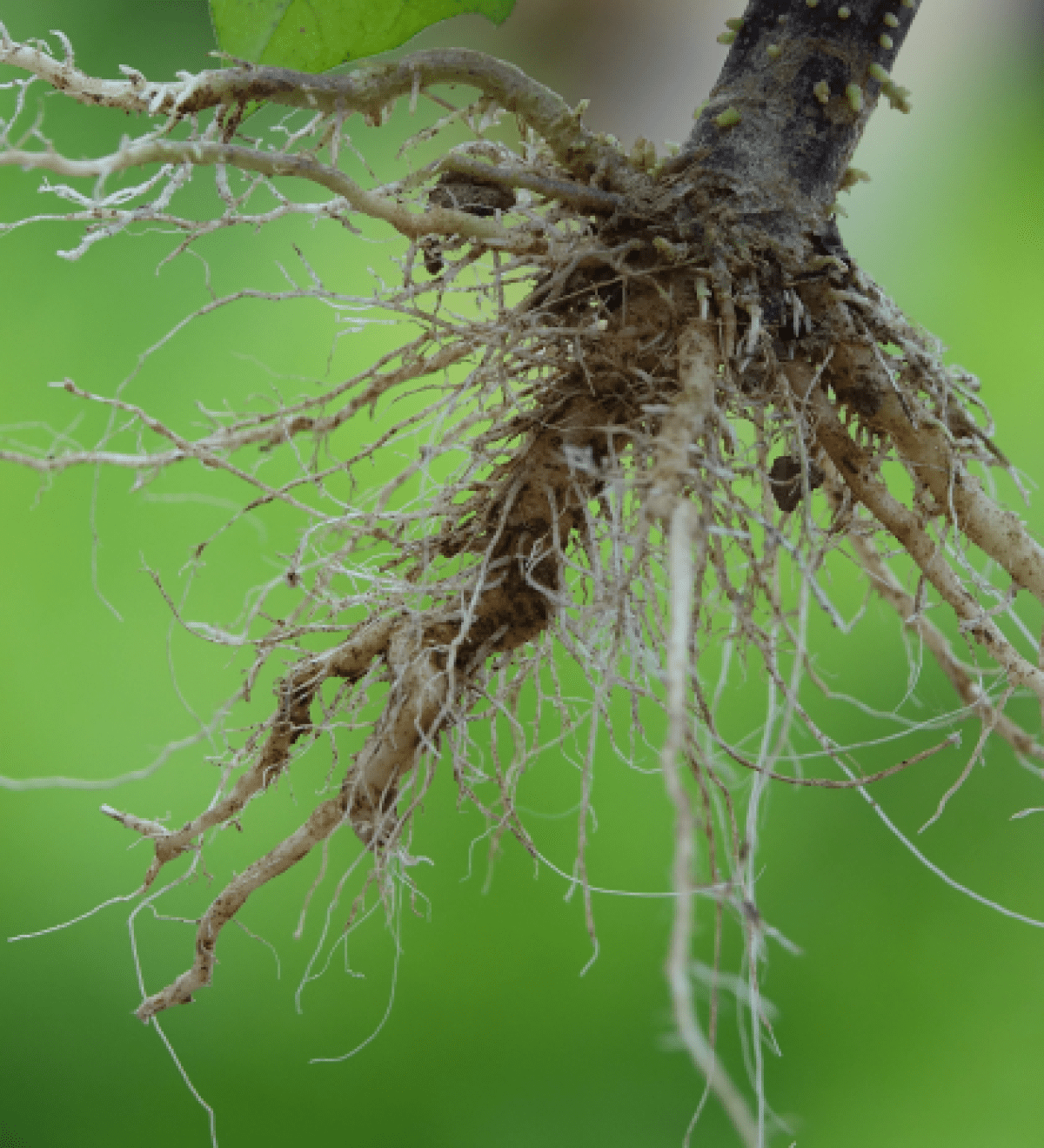

Plant diseases
Root or crown rot
Crown root rot (Rhizoctonia solani). It is a fungal disease that affects both indoor and outdoor plants, but the most common is indoor plants. The reason is poor and excessive irrigation, and this disease is often fatal to plants, and there is no effective treatment.
After crown rot, individual leaves begin to turn brown. Starting from the heart leaves, the upper parts of the plant wither and finally die. Inside the root, you can clearly find reddish-brown rotting spots. These factors disrupt the supply of water to plants. Symptoms of crown rot appear in the spring, very soon after flowering. Healthy plants growing next to infected plants is typical of the disease. In warm spring weather, initial losses appear after 4-6 weeks.
One of the crops most susceptible to infection is strawberries.
Plant disease detection service using artificial intelligence
By clicking here below you can check various diseases of apple leaves. Discover artificial intelligence and agriculture


Artificial intelligence and agriculture
Discover the power of artificial intelligence and agriculture
Care instructions
We provide you with plant care instructions
Delivery to your door
Fast delivery service inside Jordan
Expert consultation
We provide you with consulting services from our experts
Secure payment
Safe and secure payment and transaction 100%




