Table of contents of the article
Toggle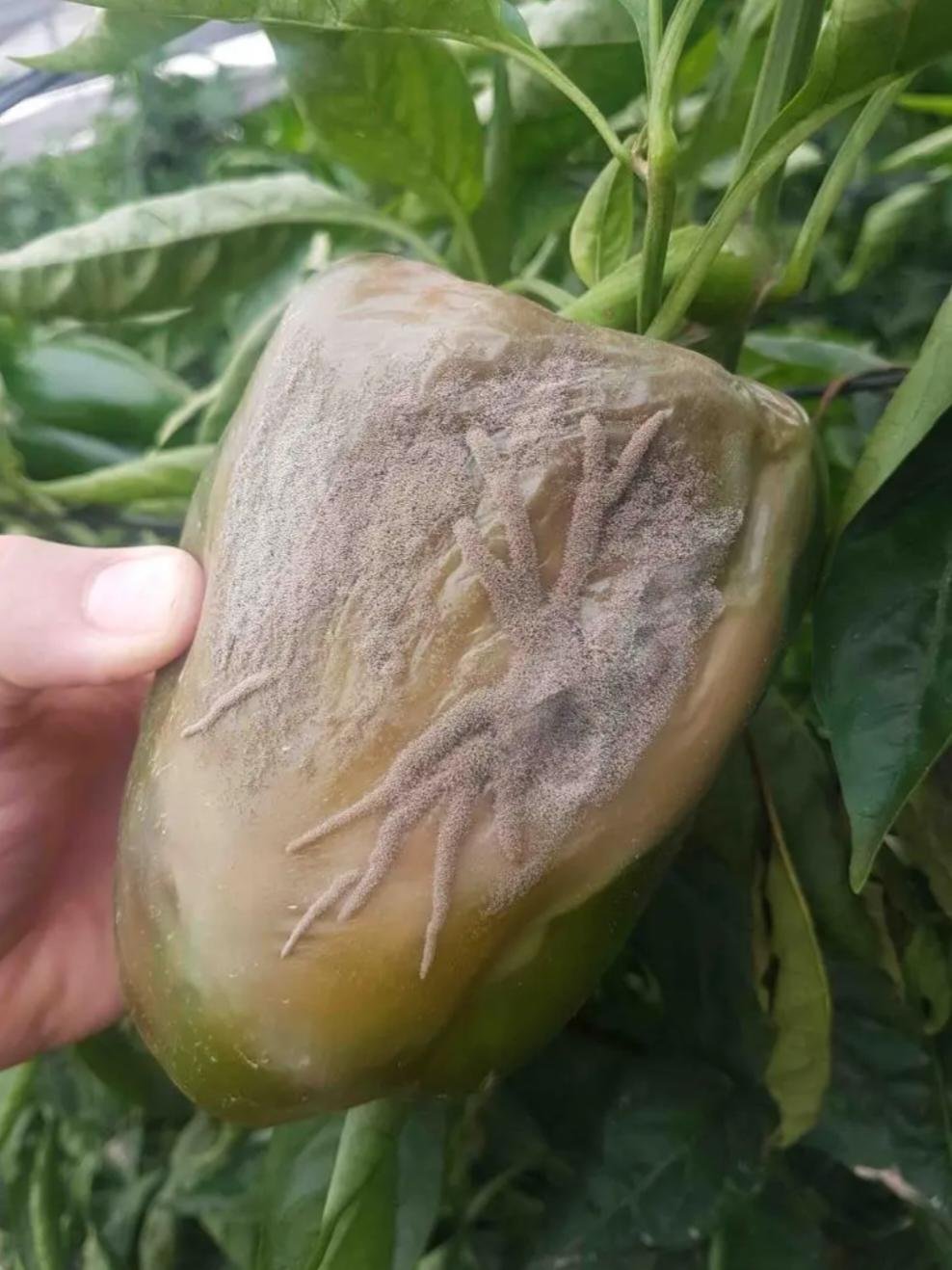
Gray mold in pepper poses a threat to pepper crops and leads to significant losses. In this article on your website, World of Plants, we learn about its symptoms and ways to prevent it.
What is gray mold in pepper?
- Chapter: Fungi
- Common name: gray mold of pepper
- Scientific name: Botrytis cinerea
- Possible host: strawberries, cranberries, blueberries, thyme, basil, sunflower, cabbage, cauliflower, peas, roses, chrysanthemums, lettuce, cucumber, squash, cantaloupe, squash, zucchini, watermelon, peppers, grapes, tomatoes, apples, And hundreds more.
Gray mold of pepper is a common fungal disease spread throughout the world. It develops primarily during the winter in open fields and enclosed structures, but tends to appear on crops growing inside covered structures. Prefers high humidity conditions.
Gray mold is a saprophytic plant, meaning it can live on dead plant debris. Their life cycle includes mycelia, conidia (for dispersal), and sclerotia (for survival). The fungus will germinate when conditions are suitable and produce conidia that spread with the release of spores from infected plant tissue by wind, water spray and mechanical means.
Gray mold tends to attack infected plant tissue. Infection generally begins after germs enter an existing wound. Spores can develop over a wide range of temperatures from 8 to 20°C. As the disease progresses, dense, gray-brown fuzzy fungi form and cause the affected tissue to dry out. Gray rot can also occur after harvest.
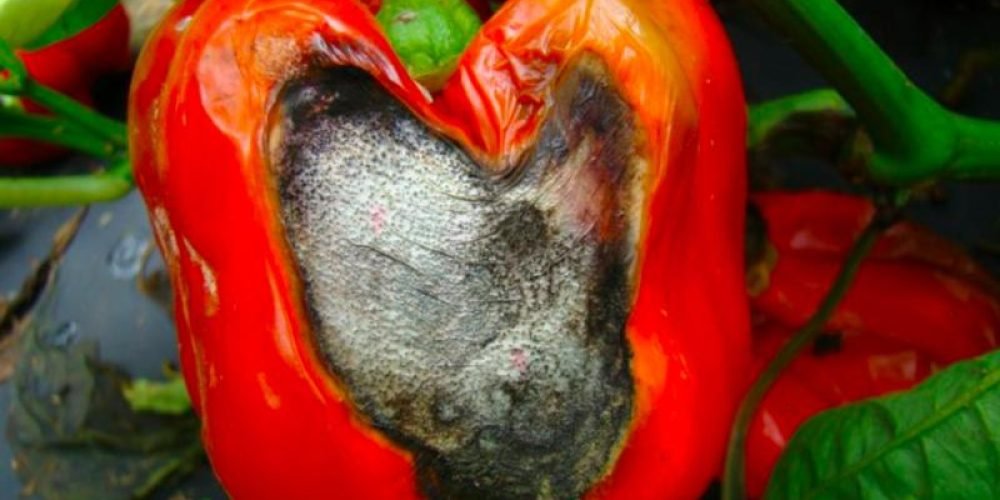
Pathological symptoms of gray mold in pepper
The infection usually begins on the flowers and young nodes in the form of a gray, plush covering of fungal spores. The flowers quickly dry up and die, and as the infection progresses, the fruits rot and lose their hardness. Especially when there is high humidity and moderate temperatures of 20-25◦C, which encourages the fungus to enter the plant tissue.
Measures to prevent gray mold disease in pepper
- It is easier to defeat insects during the early stages and is more cost effective. The field should also be monitored routinely and looked for the presence of the above signs.
- There are many methods that can be followed during the growth phase of the crop to reduce the chances of infection and its spread:
- Maintain sufficient space: You should avoid planting plants too densely in order to allow light to pass through to the plants. This allows leaves and fruits to dry quickly on humid days.
- Sterilization: Plant dirt should be removed during the plowing process. You should sterilize equipment that comes into contact with infected plants. Do not allow equipment or workers to pass through the field when plant leaves are wet.
- Air movement: In enclosed structures, foliage drying should be improved and humidification periods shortened by creating ventilated areas with mesh curtains.
- Soil drainage: The presence of standing water will promote the disease.
- Other moisture reduction methods include covering the ground with polyethylene sheets to reduce soil evaporation.
Chemical treatment of gray mold in pepper
Avoid using products with a similar active ingredient in successive treatments. This would generate resistance to the specific ingredient used.
Products used in one or more parts of the world contain the following ingredients:
Ciprodinil + fludioxonil, fenhexamide, primitanil, and iprodione.
Organic treatment for gray mold in pepper
Products containing tea tree oil sulfate and sodium hydrogen carbonate + copper
Biological treatment
*Names marked in red are considered to be highly poisonous to beneficial insects.
*Names marked in green are considered to be organic and IPM (integrated pest management) compatible.
Caution and caution should be taken when using any plant protection products (insecticides, fungicides, herbicides). It is the grower's sole responsibility to keep track of legal uses and permissions while respecting the laws in their destination countries markets. Always read the instructions written on labels and in case of inconsistency, act in accordance with the product label. Keep in mind that the information written on the label usually applies to local markets.
Prevention and treatment of gray mold disease in pepper
Gray mold disease of tomatoes is prevented by:
- Controlling the fungus that causes this disease (Botrytis).
- Use tomato varieties that can coexist with the disease.
- Good ventilation, removing infected leaves, and reducing plants inside covered houses to avoid high heat and humidity.
- Get rid of the infected parts, burn them, and avoid throwing them on top of organic fertilizer blocks.
- Take care of plants and avoid watering during late hours of the day.
- Local treatment of wounds or kidneys, depending on the degree of injury.
- Daily picking of flowers, and disinfecting refrigerators.
In conclusion, we would like to note that we, at the world of plants website, offer you all the necessary services in the world of plants, we provide all farmers and those interested in plants with three main services::-
- Artificial intelligence consulting service to help you identify diseases that affect plants and how to deal with them.
- Blog about plants, plant diseases and care of various crops ... You are currently browsing one of her articles right now.
- An application that provides agricultural consultations to clients, as well as a service for imaging diseases and knowing their treatment for free – Click to download the Android version from Google Play Store، Click to download the IOS version from the Apple App Store.
Sources
Gray mold disease on pepper - al-hakem
Vegetables - peppers - fungal diseases - gray mold - agricultureegypt
Gray mold – agrio