Table of contents of the article
ToggleSooty mold (black mold) is a fungal disease that affects many plants and greatly affects the quality of the crop. This article from the “WORLD OF PLANTS” website provides an explanation of the causes of sooty mold (black mold) on lemons, symptoms, causes, control, and effective prevention and control methods.
Causes of sooty mold (black mold) on lemon
- Disease name: sooty mold (black mold)
- Scientific name: pezizomycotina
- Type of disease: fungal
- Disease family: Pezizomycetes
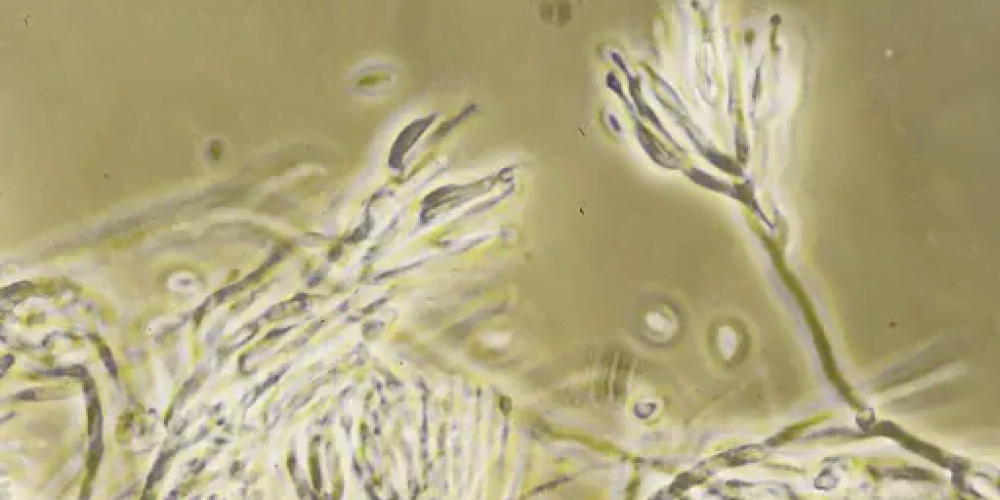
considered as pezizomycotina Non-parasitic fungi, they derive their food from the secretions of insects and plants. The most common food for these fungi is honeydew, which is a liquid secretion released from the anus of some types of insects and some types of leafhoppers.
Symptoms of sooty mold (black mold) on lemon
Dark fungal deposits appear on the leaves, coloring the leaf surface in different shades of black. As the infection progresses, the fungi cover all the leaves. Because they are considered non-pathogenic parasites, they do not show any disease symptoms on the tree as they do not colonize in plant tissues.

Development cycle of sooty mold (black mold) on lemon
These fungi reproduce by means of ascospores and conidia. Some insects, such as ants, aphids and whiteflies, tend to protect the fungal colonies so that they can attack the phloem fluid of the plant.
Suitable conditions for the spread of sooty mold (black mold) on lemon
Mold grows in humid conditions resulting from irrigation water or rainwater, and (15-20) degrees Celsius is considered the optimal temperature for mushroom growth.
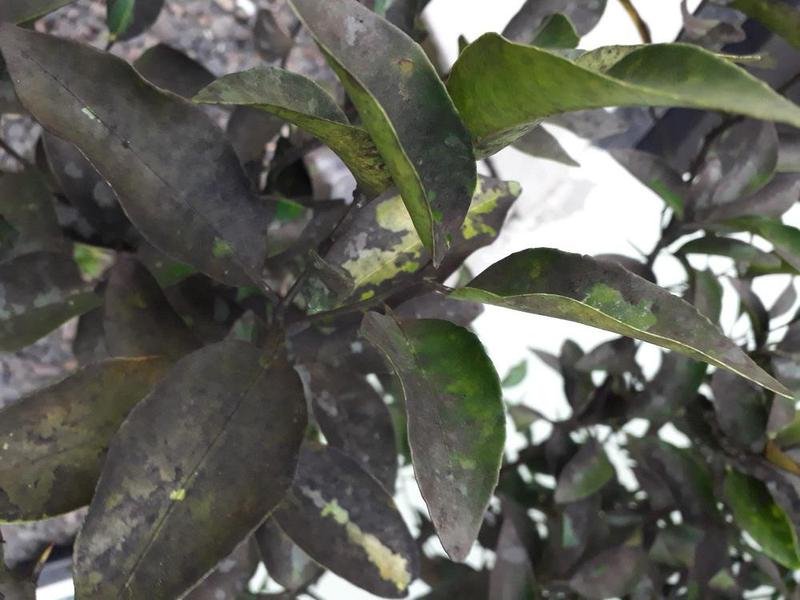

Losses resulting from the spread of sooty mold (black mold) on lemons
This fungus blocks sunlight from the leaves, which prevents the leaves from carrying out the photosynthesis process, by covering the leaves, and also prevents them from breathing and exchanging gases with the atmosphere, which may lead to the death of the plant.
Controlling sooty mold disease (black mold) on lemon
- Isolate the infected plant to avoid its spread in the field.
- Use organic neem oil to repel insects that protect fungal colonies and even limit the growth of fungi.
- Spray insecticidal soap on infected plants and rinse with water to remove the mold.
- Use pesticides that contain organophosphates, such as malathion, to prevent insects from feeding on the plant.
Preventive measures for sooty mold (black mold) on lemon
- Good fertilization of the plant to combat parasites that attack the plant.
- Irrigate trees in moderation to avoid providing a suitable environment for fungus growth.
- Ensure there is a distance between trees in the field to avoid transmission of the disease between nearby trees.
- Sterilizing agricultural tools to ensure that the disease is not transmitted.
In conclusion, we would like to note that we, at the world of plants website, offer you all the necessary services in the world of plants, we provide all farmers and those interested in plants with three main services::-
- Artificial intelligence consulting service to help you identify diseases that affect plants and how to deal with them.
- Blog about plants, plant diseases and care of various crops ... You are currently browsing one of her articles right now.
- An application that provides agricultural consultations to clients, as well as a service for imaging diseases and knowing their treatment for free – Click to download the Android version from Google Play Store، Click to download the IOS version from the Apple App Store.
Sources:
Sooty Mold – plantix
Sooty Mold – UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AGRICULTURE AND NATURAL RESOURCES