Table of contents of the article
ToggleGray mold is a fungal disease that affects many plants, including lemon, leading to damage to leaves and fruits. This article from the “WORLD OF PLANTS” website provides an explanation of the causes of gray mold disease in lemons and effective methods of prevention and treatment.
Causes of gray mold disease in lemon
- Disease name: gray mold
- Scientific name:Botrytis
- Type of disease: fungal
- Disease family: cinerea Botrytis
The fungus is transmitted through the soil, where it moves to infect all parts of the plant, and the lower leaves are considered the most susceptible to infection, especially leaves injured mechanically or through cold and frost.
Symptoms of gray mold disease in lemon
It begins to appear in the form of water-soaked spots on the leaves. They are initially white and then gradually change to grey, until they cover most of the leaf and cause it to wilt. The fungus attacks the flowers and small fruits of lemon and is characterized by its gray to greenish-gray spores. The fungus can develop in the flowers. Or on young branches, gray rot reduces fruit set and damages young fruits, leading to the formation of raised areas or ridges on the peel.

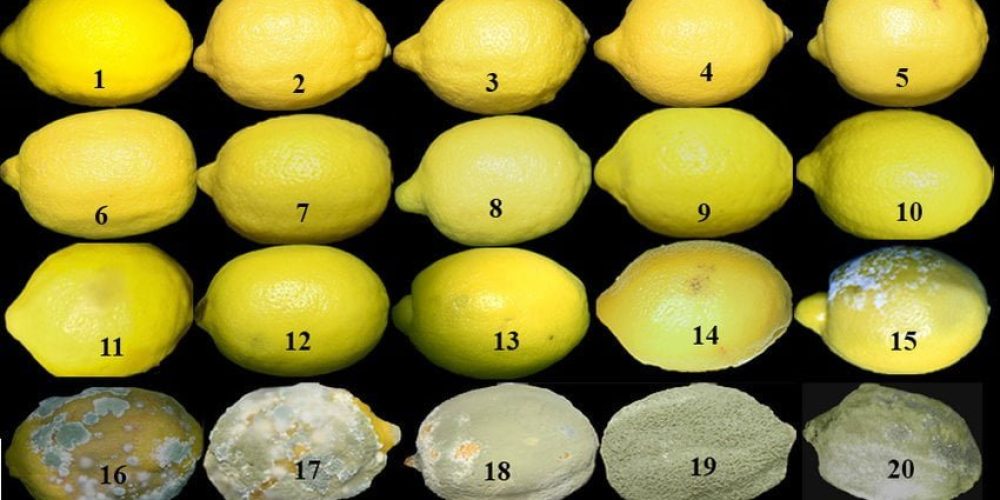
Suitable conditions for the spread of gray mold disease in lemon
Infected petals are the main source of infection for fruits and branches, as the fungus lives in conditions of humidity and cold for long periods. (15-20) degrees Celsius is considered the optimal temperature for mushroom growth. Excessive irrigation and shade also increase the level of the disease.
Development cycle of gray mold disease in lemon
In the presence of suitable weather conditions, the fungus develops, as the spores spread, forming a gray layer on the fruits, stems, or leaves. It can develop to reach the roots, and the fungus also lives on decomposing organic materials.
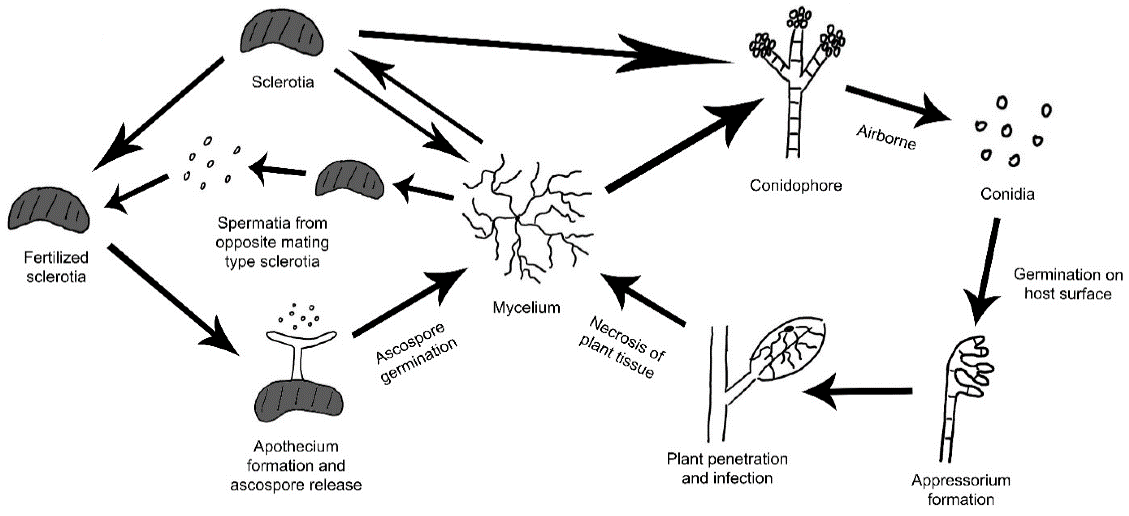
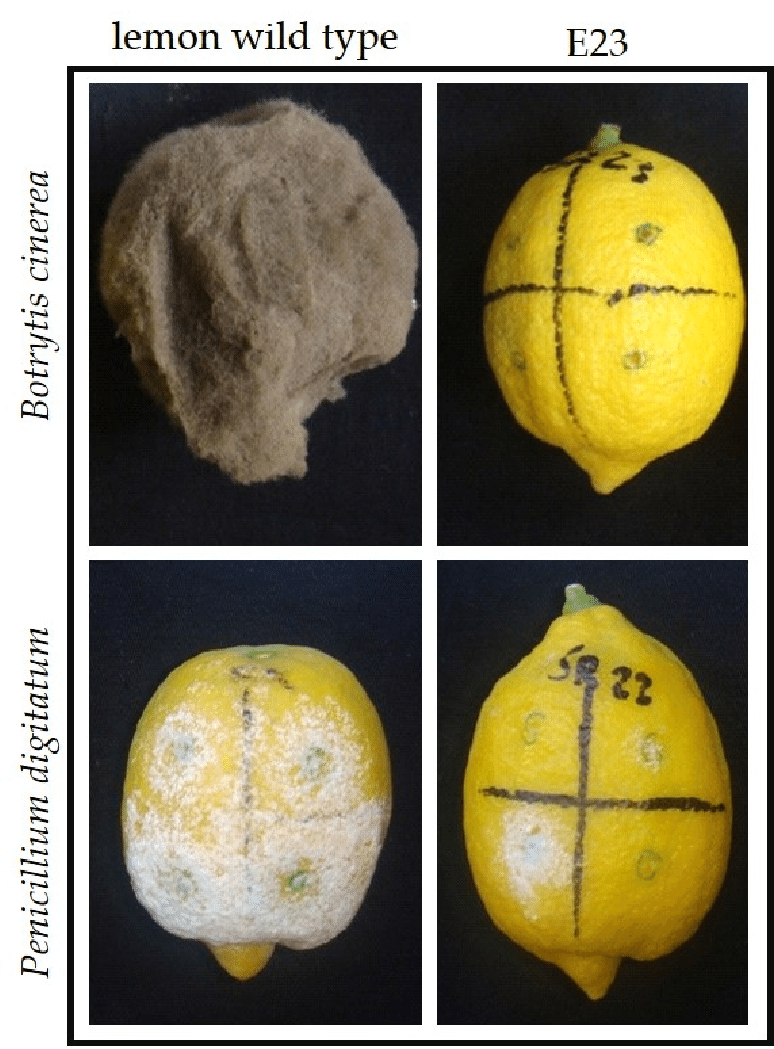
Symptoms of the disease sometimes appear during storage, which increases losses, and in some sensitive varieties, it may cause complete crop failure.
Controlling gray mold disease in lemon
The use of biocides is very effective in combating the fungus, and in the case of early infection, chlorothalonil can be used sparingly through foliar spraying to avoid resistance to the fungus.
Preventive measures for gray mold disease in lemon
- Use resistant and tolerant varieties.
- Maintain an appropriate distance between trees to avoid transmission of infection.
- Fertilizing and using mulch in an appropriate manner.
- Avoid excessive watering.
- Applying copper fungicides before rain is expected reduces the incidence of gray mold.
In conclusion, we would like to note that we, at the world of plants website, offer you all the necessary services in the world of plants, we provide all farmers and those interested in plants with three main services::-
- Artificial intelligence consulting service to help you identify diseases that affect plants and how to deal with them.
- Blog about plants, plant diseases and care of various crops ... You are currently browsing one of her articles right now.
- An application that provides agricultural consultations to clients, as well as a service for imaging diseases and knowing their treatment for free – Click to download the Android version from Google Play Store، Click to download the IOS version from the Apple App Store.
Sources:
Botrytis Diseases And Disorders – UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AGRICULTURE AND NATURAL RESOURCES
Rind distortion of lemon caused by Botrytis cinerea Pers – 1stfruits




